The digital content explosion isn’t slowing down. The global digital content creation market has grown from $27.1 billion to an expected $90.4 billion by 2033, driven by organizations generating exponentially more digital assets each year. When you’re managing thousands of images, videos, documents, and multimedia files, the question isn’t whether you need digital asset management, but whether your DAM system has the database architecture to handle your growing demands.
Do digital asset management systems need a database? Absolutely. Modern DAM platforms require sophisticated database infrastructure to organize, retrieve, and optimize digital assets at enterprise scale. Without a robust database architecture, even the most feature-rich DAM becomes a glorified file storage system that can’t deliver the performance, automation, or intelligence your teams demand.
This isn’t just about storage anymore. AI-powered metadata generation, real-time personalization, and lightning-fast search capabilities all depend on advanced database technologies that transcend traditional file systems.
What Role Do Databases Play in DAM Systems?
Digital asset management systems rely on databases as their operational backbone. While many people think of databases as simple storage containers, they’re actually sophisticated engines that power every aspect of modern DAM functionality.
The database serves as the central nervous system that connects your assets to their metadata, tracks user permissions, manages version histories, and enables the intelligent search capabilities that make or break user adoption. Without this foundation, you’re essentially running a digital filing cabinet instead of a strategic content operations platform.
Here’s what databases enable in modern DAM systems:
- Metadata Storage and Relationships: Databases store complex metadata schemas that describe your assets, from basic file information to custom business taxonomies and AI-generated tags
- Lightning-Fast Retrieval: Advanced indexing and query optimization deliver sub-second search results even across millions of assets
- Version Control and Audit Trails: Complete history tracking of every change, approval, and usage across your asset lifecycle
- Role-Based Security: Granular permission systems that control who can access, edit, or distribute specific content
- Asset Relationships: Smart linking between related assets, campaigns, and projects that improves content discovery and reuse
The difference between file storage and database-driven DAM becomes obvious when teams start scaling. A simple folder structure might work for hundreds of files, but enterprise organizations managing millions of assets need the performance and intelligence that only sophisticated database architecture can provide.
Types of Databases Powering Modern DAM Systems
Not all databases are created equal, especially when it comes to handling the diverse requirements of digital asset management. The choice between different database architectures can dramatically impact your DAM’s performance, scalability, and feature capabilities.
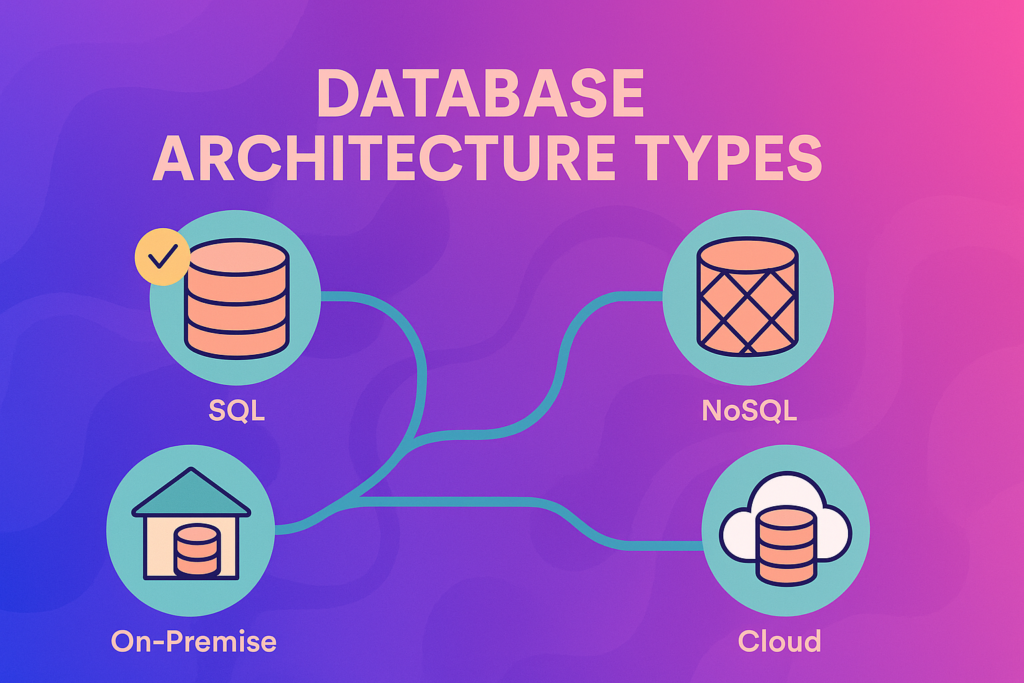
SQL vs NoSQL: The Great Database Divide
Relational (SQL) Databases excel at managing structured metadata and complex relationships between assets. They’re perfect for enforcing data consistency and handling intricate permission schemes. SQL databases shine when you need:
- Complex asset relationships and hierarchies
- Strict data integrity and ACID compliance
- Advanced reporting and analytics capabilities
- Integration with existing enterprise systems
NoSQL Databases offer flexibility for unstructured content and rapid scaling. Document-based NoSQL systems can store rich metadata without predefined schemas, making them ideal for diverse asset types and evolving business needs. Research from IBM shows NoSQL databases particularly excel at:
- Handling diverse file types and metadata structures
- Scaling horizontally across global teams
- Supporting real-time collaboration features
- Managing large volumes of unstructured data
Cloud vs On-Premise: Location Matters
Cloud-Native Databases provide automatic scaling, global distribution, and reduced infrastructure overhead. They’re particularly valuable for organizations with distributed teams or variable workloads. According to recent analysis, cloud databases offer:
- Automatic backup and disaster recovery
- Global content delivery optimization
- Pay-as-you-scale pricing models
- Integration with AI and machine learning services
On-Premise Solutions give organizations complete control over their data and can meet strict compliance requirements. They work best for industries with specific regulatory needs or limited internet connectivity.
Hybrid Architectures combine the best of both worlds, allowing organizations to keep sensitive assets on-premise while leveraging cloud capabilities for collaboration and distribution.
How AI is Transforming DAM Database Architecture
The integration of artificial intelligence is revolutionizing how DAM databases operate, moving beyond simple storage to intelligent content understanding and automation. This shift represents one of the most significant advances in digital asset management technology.
Automated Metadata Generation
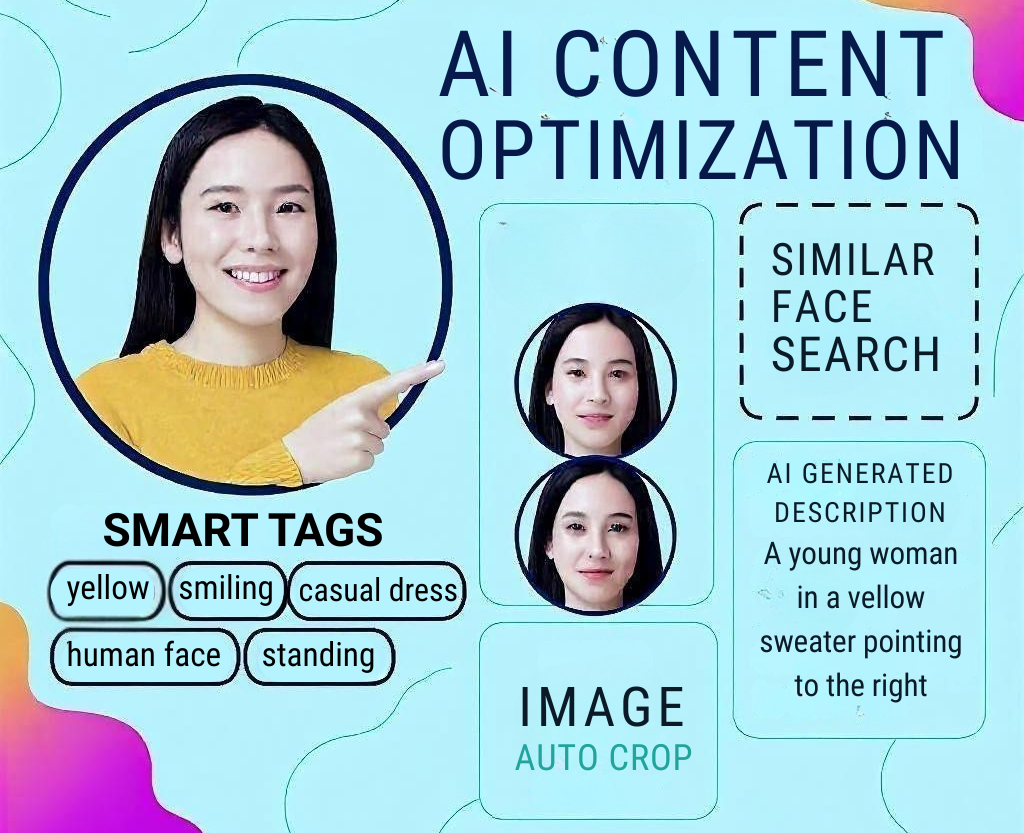
Traditional DAM systems required manual metadata entry, a time-consuming process that often resulted in inconsistent or incomplete asset information. Modern AI algorithms can now automatically analyze content and generate rich, searchable metadata, including:
- Computer Vision Analysis: Automatic identification of objects, people, text, and scenes within images and videos
- Natural Language Processing: Extraction and categorization of text content from documents and multimedia files
- Brand Recognition: Training custom models to identify specific products, logos, or brand elements
- Contextual Tagging: Understanding relationships between assets and automatically creating relevant cross-references
Intelligent Search and Discovery
AI-powered databases transform how users find and interact with content. Instead of relying solely on manual tags, intelligent systems can understand user intent and deliver relevant results even when search queries don’t match exact metadata. This includes:
- Semantic Search: Understanding the meaning behind search queries rather than just matching keywords
- Visual Similarity: Finding assets based on visual characteristics rather than textual descriptions
- Predictive Recommendations: Suggesting relevant assets based on user behavior and project context
- Multi-Modal Search: Combining text, visual, and contextual searches for more accurate results
Real-Time Content Optimization
Advanced DAM databases now support real-time content personalization and optimization. By analyzing user behavior, content performance, and business context, these systems can automatically optimize asset delivery for different channels and audiences.
5 Essential Database Features Every DAM System Needs
When evaluating DAM solutions, certain database capabilities separate enterprise-ready platforms from basic file storage systems. These features determine whether your DAM can scale with your business and deliver the performance modern teams expect.
Feature 1. Advanced Indexing and Search Optimization
Modern DAM databases must support multiple indexing strategies to ensure fast retrieval across different search types. This includes full-text indexing for document content, spatial indexing for visual similarity searches, and composite indexing for complex metadata queries. Sub-second response times should be standard even when searching across millions of assets.
Feature 2. Flexible Metadata Schema Management
Your database should support both structured and unstructured metadata without requiring schema changes for new asset types or business requirements. Flexibility becomes crucial as organizations expand their content types or integrate new data sources.
Feature 3. Comprehensive Audit and Version Control
Enterprise DAM databases must maintain complete audit trails of every asset interaction, from creation to deletion. This includes tracking who accessed what content, when changes were made, and how assets were used across different campaigns or projects.
Feature 4. Granular Permission Management
Role-based access control should surpass simple read/write permissions to include granular controls over asset usage, download rights, and collaboration features. The database should efficiently handle complex permission matrices across thousands of users and assets.
Feature 5. Intelligent Caching and Performance Optimization
Advanced caching strategies ensure consistent performance regardless of user location or asset size. This includes multi-tier caching, content delivery network integration, and intelligent prefetching based on user behavior patterns.
Database Performance Optimization in DAM
Database performance directly impacts user adoption and team productivity. Research from DAM implementations shows that organizations with optimized DAM databases see increases in productivity and a reduction in time spent managing digital assets.
Query Optimization Strategies
Effective DAM databases employ sophisticated query optimization techniques, including automated index selection, query plan caching, and parallel processing for complex searches. These optimizations ensure consistent performance even as content libraries grow exponentially.
Scalability Architecture
Modern DAM databases must handle both vertical and horizontal scaling. Vertical scaling accommodates growing file sizes and metadata complexity, while horizontal scaling supports increasing user bases and global distribution requirements.
Memory Management and Caching
Intelligent memory management becomes critical when dealing with large multimedia files and complex metadata relationships. Advanced systems use multi-level caching strategies that keep frequently accessed content readily available while efficiently managing memory resources.
Future of DAM Database Technology
The evolution of DAM database technology continues accelerating, driven by advances in AI, edge computing, and distributed systems architecture. Understanding these trends helps organizations make informed decisions about their DAM investments.
Graph Databases and Relationship Intelligence
Graph database technology is emerging as a powerful complement to traditional relational systems. By modeling assets and their relationships as interconnected nodes, graph databases enable sophisticated content discovery based on complex relationships between people, projects, brands, and campaigns.
Blockchain Integration for Digital Rights
Blockchain technology is beginning to integrate with DAM databases to provide immutable records of asset ownership, usage rights, and licensing agreements. This technology particularly benefits organizations dealing with complex intellectual property management and rights tracking.
Edge Computing and Distributed Storage
As teams become increasingly global, edge computing capabilities allow DAM databases to cache and process content closer to end users. This distributed approach reduces latency and improves performance for international teams while maintaining centralized control and security.
Choosing the Right Database Architecture for Your DAM
Selecting the best digital asset management database architecture requires careful consideration of your organization’s specific needs, growth projections, and technical requirements. The wrong choice can limit your DAM’s effectiveness and create expensive migration challenges down the road.

Assessing Your Requirements
Start by evaluating your current and projected content volumes, user base size, and performance requirements. Consider factors like global distribution needs, compliance requirements, and integration complexity with existing systems.
Don’t just count files; analyze the complexity of your metadata requirements, the diversity of your asset types, and the sophistication of your workflow automation needs. Organizations often underestimate how quickly their requirements evolve, particularly as AI automation becomes standard and teams expect intelligent content recommendations rather than basic search functionality.
Think beyond your immediate needs to anticipate future growth scenarios. Will your database architecture support real-time content personalization when you expand into new markets? Can it handle the metadata complexity that comes with AI-powered content generation and automated compliance checking? The most successful DAM implementations plan for 3–5 years of growth, ensuring their database foundation can scale not just in storage capacity but in processing sophisticated relationships between assets, users, and business contexts.
Vendor Evaluation Criteria
When evaluating DAM solutions, focus on database capabilities rather than just user interface features. Ask potential vendors about their indexing strategies, scaling approaches, and disaster recovery capabilities. Request performance benchmarks for scenarios matching your expected usage patterns.
Dig deep into their AI integration capabilities. How does their database architecture support automated metadata generation, intelligent search, and predictive content recommendations? The vendors who can demonstrate sophisticated database features like graph-based relationship modeling and real-time analytics processing are typically building for the future of content operations.
Don’t accept vague promises about “enterprise scalability” without seeing concrete evidence. Request demonstrations using datasets similar to your expected volume and complexity. Ask about their approach to global content distribution, compliance automation, and integration with existing business systems. The right vendor should be excited to discuss their database architecture because they understand it’s the foundation that enables advanced features like automated asset lifecycle management and intelligent workflow optimization.
Migration and Implementation Planning
Database migration represents one of the most complex aspects of DAM implementation, often determining whether your project delivers transformational results or becomes a costly setback. Ensure your chosen solution provides robust migration tools and professional services support to minimize disruption during the transition process. The best implementations treat migration as an opportunity to clean up metadata inconsistencies, establish proper taxonomies, and implement automation rules that will drive long-term efficiency gains.
Successful migration planning addresses both technical and organizational challenges. Your database architecture should support gradual migration approaches that allow teams to continue working while the system transitions. Look for platforms that offer advanced data validation tools, automated metadata mapping, and intelligent duplicate detection during the migration process. The most sophisticated systems can even maintain audit trails through migration, ensuring compliance requirements are met while transitioning to more powerful database capabilities that will enable future innovations in content operations.
The Bottom Line on DAM Databases
Do digital asset management systems need a database? The answer isn’t just yes; it’s that the quality and sophistication of your DAM’s database architecture will determine whether your investment delivers transformational results or becomes another underutilized technology stack.
Organizations serious about scaling their content operations need DAM systems built on modern, intelligent database foundations. These platforms unlock the full potential of your content through advanced search, automated optimization, and intelligent insights that drive better business outcomes.
The database is the engine that powers content personalization, enables AI-driven automation, and scales with your business growth. Choose wisely, because your database architecture will shape your content operations for years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions
What type of database is best for digital asset management systems? The best database type depends on your specific needs. SQL databases excel at structured metadata and complex relationships, while NoSQL databases offer flexibility for diverse content types and rapid scaling. Many modern DAM systems use hybrid approaches combining both technologies.
How does database choice affect DAM performance? Database architecture directly impacts search speed, scalability, and feature capabilities. Well-optimized databases can deliver sub-second search results across millions of assets, while poorly designed systems may struggle with even basic queries as content libraries grow.
Can DAM systems work without traditional databases? While simple file storage systems can organize assets, they lack the metadata management, search capabilities, and automation features that modern businesses require. Enterprise-grade DAM systems require sophisticated database infrastructure to deliver advanced functionality.
How do AI features depend on database architecture? AI-powered features like automated tagging, intelligent search, and content recommendations require databases capable of storing and processing complex metadata relationships. Advanced indexing and machine learning integration capabilities are essential for AI functionality.
What database security features are important for DAM systems? Critical security features include encryption at rest and in transit, role-based access controls, audit logging, and compliance certifications. The database should also support integration with enterprise identity management systems and provide granular permission controls.
How do cloud vs on-premise databases compare for DAM? Cloud databases offer automatic scaling, global distribution, and reduced infrastructure management, while on-premise solutions provide complete data control and can meet strict compliance requirements. Hybrid approaches combine the benefits of both deployment models.
Modern digital asset management platforms combine sophisticated database technology with AI-powered automation to transform how organizations manage their content operations. Discover how the right DAM foundation can accelerate your content velocity, improve asset discoverability, and ensure brand consistency across all your digital experiences. Get started with Aprimo today to see the difference intelligent content operations can make for your organization.


